Wikimedia Commons
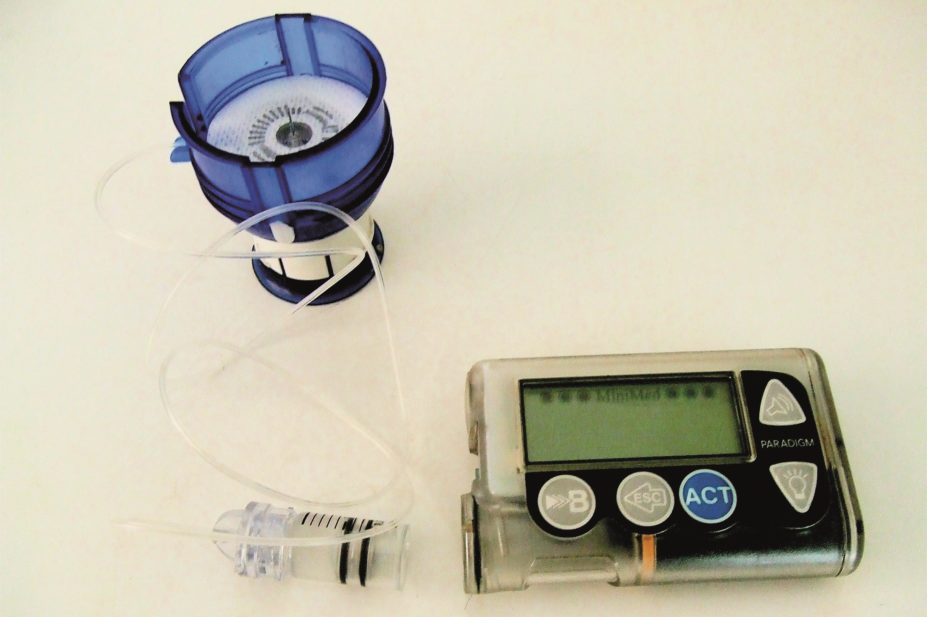
Insulin pumps have been increasingly used in paediatrics in the past 15 years, but availability and support for these devices varies between countries.
An international team of researchers compared data on 54,410 children and adolescents from three diabetes registries in the United States, Germany and Austria, and England and Wales. In all three registries, glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels were significantly lower among insulin pump users than injection users, but the rate of pump use in England and Wales was around only 30% of that in the other countries.
HbA1c levels were also highest in England/Wales at a mean of 8.9mmol/mol vs 8.3mmol/mol and 8.0mmol/mol in the United States and German/Austrian registries, respectively.
Writing in Diabetologia (online, 7 November 2015)[1]
, the researchers say the lower level of pump use in England/Wales may be due to relatively restrictive national guidelines on their use in paediatrics.
References
[1] Sherr JL, Hermann JM, Campbell F et al. Use of insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes and its impact on metabolic control: comparison of results from three large, transatlantic paediatric registries. Diabetologia 2015. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3790-6