Courtesy of Dr Seokheun Choi
Exercise in people with insulin-dependent diabetes can lead to hypoglycaemia; hence, blood glucose needs careful monitoring during and after physical activity.
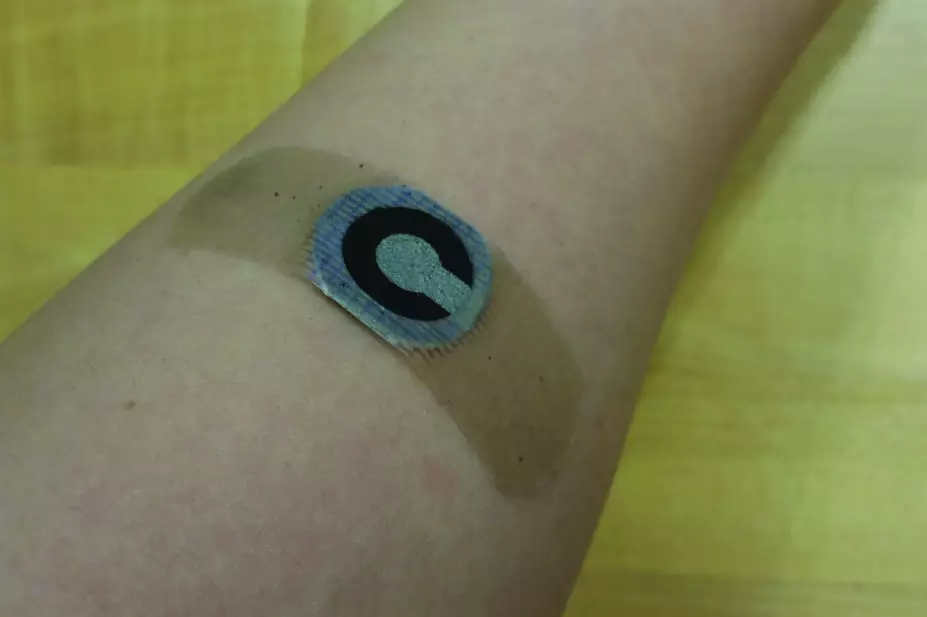
Researchers developed a self-powered disposable patch incorporated into a standard plaster to non-invasively measure glucose in sweat during exercise. The device absorbs sweat and uses it to generate an electrical current, which corresponds with glucose concentration and is measured using a digital multimeter.
In a paper in Micromachines (31 August 2017), designers tested the patch on two healthy human subjects during exercise and compared the results with blood glucose measurements taken 30 minutes into exercise[1]
. They showed that there was a strong correlation between sweat and blood measurements.
The team said the device showed potential for continuous glucose monitoring but needed further refinement including testing at hypoglycaemic glucose concentrations and full integration of the detector into the patch.
References
[1] Cho E, Mohammadifar M & Choi S. A single-use, self-powered, paper-based sensor patch for detection of exercise-induced hypoglycemia. Micromachines 2017;8:265. doi: 10.3390/mi8090265